Examining the Case Type Backlog
11 Tasks
30 mins
Scenario
You just arrived on the GoGoRoad application development project as a Pega Business Architect.
GoGoRoad is a membership-based automotive service company. GoGoRoad helps members when they are stranded with automotive trouble by providing the services necessary to quickly get them back on the road. Over the last several years, business for GoGoRoad has grown, and its current process and procedures are no longer sufficient. The GoGoRoad membership team cannot process new memberships quickly enough to get distressed travelers in the system before they get frustrated and seek service elsewhere. Customer membership renewals are not being processed, which forces customers to reapply to access the service they desperately need. The Service team is experiencing bottlenecks in the dispatch and billing processes. To ensure its continued and future growth, GoGoRoad engaged Pega to develop and build an application to transform both the membership and service aspects of its business.
The content of discussions that take place between stakeholders from GoGoRoad and the Pega Sales team during sales meetings and early in the Pega Express Discover phase is communicated to the application implementation team in a document called the Case Type Backlog.
The Case Type Backlog is an Excel spreadsheet that conveys the fundamental building blocks of an application in terms of the three pillars of Pega Platform™: Microjourneys®, Personas and Channels, and Data and Interfaces. The Case Type Backlog details the assumptions made regarding the application, and Minimum Lovable Product (MLP) builds. Finally, the Case Type Backlog synthesizes all of the inputs and, through a series of proprietary macros, outputs estimates for the number of development hours for MLP1 and beyond. The Case Type Backlog details the scope of the Pega application project in a single, living document.
The Case Type Backlog is delivered to the application implementation team at the Sales to Delivery meeting. Information in the Case Type Backlog is the basis for future meetings with project stakeholders from both Business and IT as they align over project capabilities and requirements. As the project evolves and additional requirements are gathered during Directly Capture Objectives (DCO) meetings, the Case Type Backlog, as well as the size and scope of the project, is likely to evolve as well.
As a Business Architect newly assigned to a Pega project, the easiest way to educate yourself about the application is by examining the Case Type Backlog. Examine the GoGoRoad Case Type Backlog to educate yourself about the scope of the GoGoRoad project, which serves as the basis for the Challenges ahead. Additionally, use the link to the Case Type Backlog spreadsheet found in the Pega Express Tooklit to build a Case Type Backlog for a project of your choosing.
Detailed Tasks
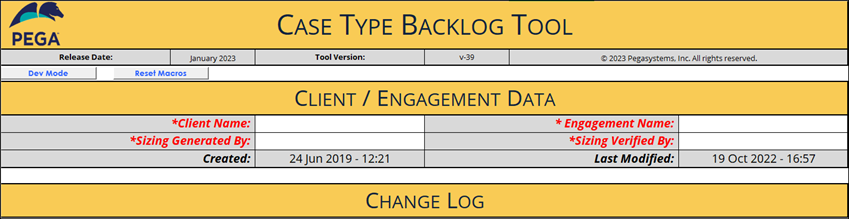
1 Explore the Project Summary tab
- Download the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook to your desktop.GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx (106.08 KB)Note: For security, the macros in this Case Type Backlog are disabled. Macros are enabled for Case Type Backlog workbooks downloaded directly from the Pega Express Toolkit website. - Open the workbook, and then click the Project Summary tab.
- Review the Client Name, Engagement Name, and Change Log.
- Download the Case Type Backlog workbook from the Pega Express Toolkit website to your desktop.
Tip: Enable the Macros associated with the Case Type Backlog Tool in order for the Excel spreadsheet to transfer information across the various tabs.
- Think of a project you have worked on in the past or a project to which you are currently assigned.
Envision this project as a Pega Platform application and use it to build your own Case Type Backlog. - Open the Case Type Backlog, and then in the Client Name field, enter the name or the project.
- In the Sizing Generated By field, enter your name.
As shown in the following figure, the Project Summary tab contains basic information about the project:
Note: The Project Summary tab also includes information about when the Case Type Backlog document was modified.
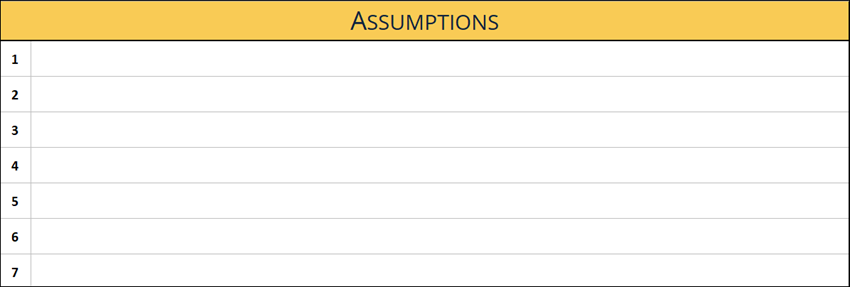
2 Explore the Assumptions tab
In the Assumptions tab, document any information about any project or program-level assumptions that were agreed upon for various aspects:
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Assumptions tab. - Review the assumptions made for the GoGoRoad project, making special note of assumptions made for MLP1.
- In your own Case Type Backlog, document any information about any project or program-level assumptions that were agreed upon for various aspects of your project, including data migration, application branding, and channel delivery.
The following figure shows the Assumptions tab:
Note: Information contained in the Assumptions tab comes from the Sales to Delivery meeting, which gives the Business Architect and other members of the implementation team a good understanding of what limitations were taken into consideration when project size and cost were calculated.
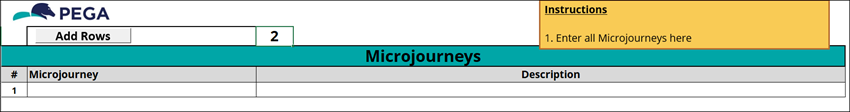
3 Explore the Microjourneys tab
On the Microjourneys tab, document the process that must be redesigned to achieve the outcomes for the customer addressed by the project:
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Microjourneys tab. - Review the Microjourneys that were identified for the GoGoRoad project:
- In the Microjourney column, define a Microjourney for each identified outcome for the customer.
- In the Description column, enter assumptions and exceptions that influence the workflow, volume areas to consider, and requirements of the client.
- In your own Case Type Backlog, document the Microjourney and the description for your project.
The following figure shows the Microjourneys tab:
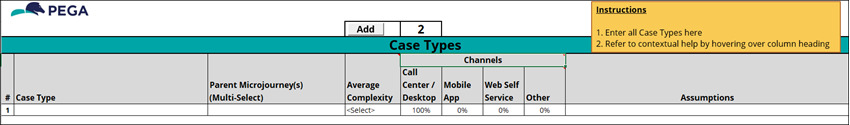
4 Explore the Case Types tab
On the Case Types tab, list the Case Types, their related Microjourneys, the expected development complexity, expected Channel usage, and related assumptions:
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Case Types tab. - Review the information provided for the Case Types identified for the GoGoRoad project:
- In the Parent Microjourney(s) column, review the selected Microjourney.
- In the Average Complexity column, review the selected levels:
Note: The delivery for MLP1 is expected to have a complexity level of OOTB or Low.
- OOTB (Out-of-the-box)
- Low
- Medium
- High
- Complex
- In the Channels column, in the sub-columns, review the expected exposure to users for each channel type in which users receive the Cases.
- In the Assumptions column, review any assumptions that have been made about the Case Types, their relationship to each other, and their delivery over the MLPs of the project.
- In your own Case Type Backlog, document the Case Types for your project:
- Select one or more Parent Microjourney(s).
- Select an Average Complexity.
- In the Channels column, assign an expected exposure to users for each channel type in which users receive the Cases.
- In the Assumptions column, document any assumptions that have been made about the Case Types, their relationship to each other, and their delivery over the MLPs of the project.
An example of the Case Type tab is shown in the following figure:
Note: There is not always a one-to-one relationship between Case Types and Microjourneys. The Case Type tab is the place to define the relationship between the Case Types that you develop in App Studio and the Microjourneys that were identified from the customer journey and the desired strategic outcome.
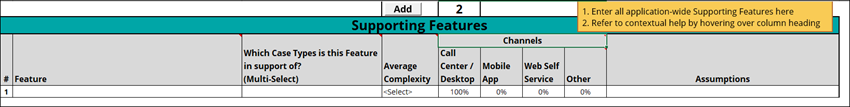
5 Explore the Supporting Features tab
On the Supporting Features tab, list the application-wide supporting features that are identified during the Discovery phase of the project.
The Supporting Features tab provides information and requirements for the overall functionality of the Case Type workflow as it relates to Pega's capabilities in workflow automation and AI-powered decisioning. This information is especially important to the application implementation team as it is the foundation for all of the application development work within the application's Case Types.
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Supporting Features tab. - Review the information provided for the Supporting Features identified for the GoGoRoad project:
- In the Case Types column, review the Case Type associated with each feature.
- In the Average Complexity column, review the selected levels:
Note: The delivery for MLP1 is expected to have a complexity level of OOTB or Low.
- OOTB (Out-of-the-box)
- Low
- Medium
- High
- Complex
- In the Channels column, in the sub-columns, review the expected exposure to users for each channel type in which users receive the Cases.
- In the Assumptions column, review any assumptions that have been made about the Case Types, their relationship to each other, and their delivery over the MLPs of the project.
- In your own Case Type Backlog, document a couple of Pega features that you identify as being vital to your project's application.
Note: Focus on features that you implemented in your Low-Code Maker Application build. These features include Approve/Reject functionality, automated email notifications, automated routing, and service-level agreements.
- Select one or more Case Types that each feature supports.
- Select an Average Complexity.
- In the Channels column, assign an expected exposure to users for each channel type in which users receive the Cases.
- In the Assumptions column, document any assumptions that have been made about the Case Types, their relationship to each other, and their delivery over the MLPs of the project.
The Supporting Features tab is shown in the following figure:
Note: For the Pega Business Architect, the features on the Supporting Features tab greatly influence, but do not completely define, the way you transform the organization's existing processes into transformed workflows that capitalize on Pega automation and AI-based decisioning features. If you can improve a workflow using Pega features and features that are not on the Supporting Features tab, do not hesitate to communicate your ideas to the relevant stakeholders from both the Business and IT project teams.
6 Explore the Interfaces tab
On the Interfaces tab, list the external systems of record (SORS) with which the application interfaces. The SORs are categorized as either a Connector or a Service:
- A Connector is an interface in which this Pega application initiates a request to some other data source or application •
- A Service is an interface in which some other application initiates a request to this Pega application.
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Interfaces tab. - Review the information provided for the Interfaces identified for the GoGoRoad project:
- In the Service of Connector column, review the selection of Connector or Service.
- In the Interface/Data Source Type column, review the selected source type of the interface.
Note: The list of Source Types depends on your selection for the Service or Connector column. The most popular choices for Connectors are SOAP or REST.
- In the Complexity column, review the selection of Low, Medium, or High.
- In the Interface Data Source Exists? column, review the selection of Yes, No, or Unknown.
- In the Assumptions column, review any assumptions that have been made about the interface.
- To the extent possible, document the interfaces you identified for your application in your own Case Type Backlog.
The following figure shows the Interfaces tab:
Note: This interface information is of most interest to the System Architects of the implementation team, but it is helpful for Business Architects to have an idea of the complexity of this aspect of the project.
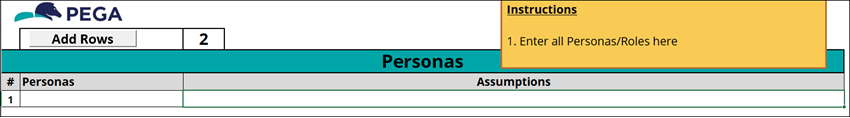
7 Explore the Personas tab
On the Personas tab, list different broad user groups that are expected to interact with the application and Case Types. Identify each user group, their relationship to one another, and any other assumptions made regarding their role within the application:
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Personas tab. - Review the information provided for the Personas identified for the GoGoRoad project, and the Assumptions made regarding the user group.
- In your Case Type Backlog, document the Personas identified as users of your application. Details any related assumptions.
An example of the Personas tab is shown in the following figure:
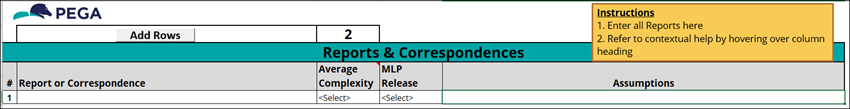
8 Explore the Reports tab
In the Reports tab, list custom reports and correspondence identified as important to the successful adoption and integration of the application.
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Reports tab. - Review the information provided for the Reports or Correspondence identified for the GoGoRoad project.
- In the Average Complexity column, review the selected levels:
- OOTB (Out-of-the-box)
- High
- Medium
- Low
- In the MLP Release column, review the MLP release.
- In the Assumptions column, review any assumptions that have been made about the interface.
- In the Average Complexity column, review the selected levels:
- In your own Case Type Backlog, document at least one custom report that assists in operational analysis by project stakeholders.
The following figure shows an example of the Reports tab:
Note: The Reports tab does not list out-of-the-box reports that are available with Pega Platform but rather custom reports that the implementation team must build. The Reports tab details the report name, development complexity, expected release, and any assumptions made about the report.
9 Explore the Work Backlog tab
The Work Backlog tab consolidates details entered into the earlier tabs of the Case Type Backlog spreadsheet.
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Work Backlog tab. - Review the columns of the Work Backlog tab for the GoGoRoad project:
- C or F: Automatically populates entries from the Supporting Features tab as either a Case Type or Feature.
- Microjourney: Automatically populates entries from the Supporting Features tab with entries from the Microjourneys tab through Case Type information.
- CaseType / Feature: Automatically populates from the Supporting Features tab.
- Which Case Type is this Feature in support of?: Automatically populates Case Types from the Supporting Features tab.
- Average Complexity: Automatically populates from the Supporting Features tab.
- Interfaces columns: Interfaces populate from the Interfaces tab. Review how Interfaces were associated with Supporting Features.
- Personas columns: Personas populate from the Personas tab. Review how Personas were associated with Supporting Features.
- Channels columns: Automatically populates entries from the Case Types tab. Associates the Channels with Supporting Features through Case Type information.
- Biz Value: Review the selection of Low, Medium, or High
- MLP Release: Review selection of MLP1, MLP2, MLP3, MLP4, or Future.
- Sizing Assumptions: Enter any assumption about features as it relates to the sizing of the project. The Assumptions column justifies the value assigned in the Biz Value column.
- In your Case Type Backlog, examine the Work Backlog tab to confirm information from the preceding tabs is correctly consolidated.
- Enter an X where identified Interfaces relate to Supporting Features or Case Types.
- Enter an X where identified Personas relate to Supporting Features or Case Types.
- Select a Bix Value for each Supporting Feature or Case Type.
- Select a Release for each Supporting Feature or Case Type.
- Add any assumptions that you feel are relevant to project sizing.
An example of the Work Backlog tab is shown in the following figure:
Note: As a Business Architect, the Work Backlog acts as a single-tab project summary. You can use the previous tabs for supporting information, especially regarding made assumptions.
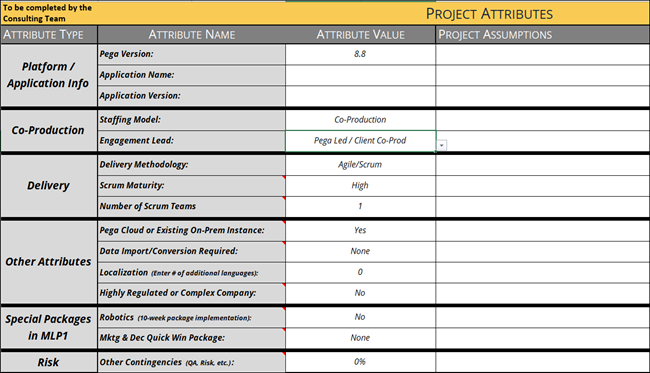
10 Explore the Project Attributes tab
On the Project Attributes tab, provide additional information about the project as it relates to application development and deployment:
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Project Attributes tab. - In the Attribute Type column, review the information provided for the project attributes as they relate to the GoGoRoad project:
Attribute Type Actions Platform/Application Info - In the Pega Version field, enter the version number of the Pega application.
- In the Application Name field, enter the name of the application.
- In the Application Version field, enter the major and minor version numbers of the application.
Note: The first version of an application is always 01.01Co-Production - In the Staffing Model list, select one of the following values:
- Co-Production
- Non Co-Production
- In the Engagement Lead list, select the type of lead:
- Pega Led/Client Co-Prod
- Partner Led/Client Co-Prod
- Pega Led
- Partner Led
Delivery - In the Delivery Methodology list, select a delivery type:
- Agile/Scrum
- Waterfall/Other
- In the Scrum Maturity, select a value:
- High
- Medium
- Low
- In the Number of Scrum Teams field, enter a number.
Other Attributes - In the Pega Cloud or Existing On-Prem Instance list, select a value:
- Yes
- No
- In the Data Import/Conversion Required, select the level of effort required:
- None
- Low
- Medium
- High
- In the Localization field, enter the number of additional languages.
- In the Highly Regulated or Complex Company list, select a value:
- Yes
- No
Special Packages in MLP1 - In the Robotics list, select a value:
- Yes
- No
- In the Mkt & Dec Quick Win Package list, select a value:
Risk In the Other Contingencies field, enter a percentage. -
In your Case Type Backlog, review and select some possible choices for the different Attribute Types associated with your project.
The Project Attributes tab comes populated with some default values, as shown in the following figure:
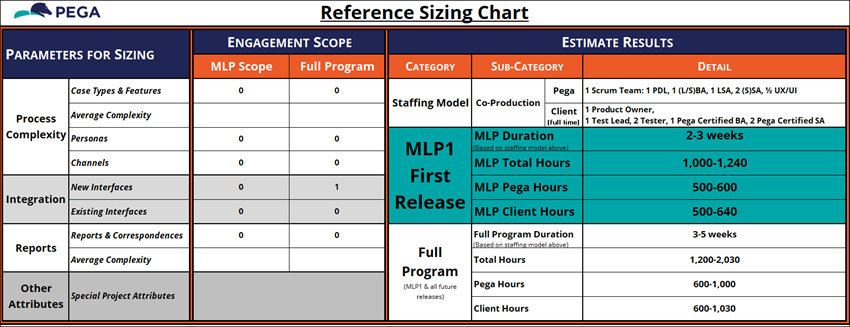
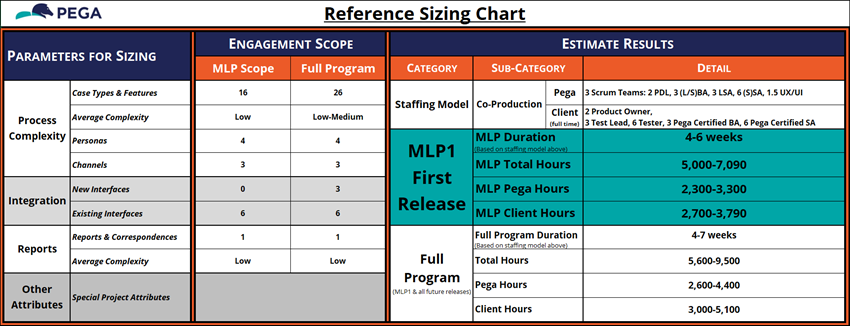
11 Explore the Reference Sizing tab
The Reference Sizing tab is one of the most important of the Case Type Backlog spreadsheet.
- Review the Reference Sizing Chart's default values, as shown in the following figure:
These values autopopulate based on the information entered into the preceding tabs. The Case Type Backlog workbook comes preconfigured with macros that generate estimates for the number of development hours required to go live for MLP1 and then the full program. These calculations are based on years of Pega Platform implementations and, with correct input values, are quite accurate.
- In the
GoGoRoad_CaseTypeBacklog_Challenge.xlsx workbook, click the Reference Sizing Chart tab.
The values provided on the Reference Sizing Chart tab should resemble those in the following figure: - On the Reference Sizing Chart tab, review the information provided for the GoGoRoad project:
- Parameters for Sizing
- Process Complexity: Calculated from the Work Backlog tab.
- Integration: Calculated from the Interfaces tab.
- Report: Calculated from the Report tab.
- Other Attributes
- Estimate Results
- Staffing Model: Based on the delivery value of the Number of Scrum Teams field on the Project Attributes tab.
- MLP1 First Release: Values for the MLP1 Release are based on proprietary calculations built into the Case Type Backlog workbook.
- Full Program: Values for the Full Program are based on proprietary calculations built into the Case Type Backlog workbook.
- Parameters for Sizing
- In your own Case Type Backlog, enter values for the Engagement Scope columns on the Reference Sizing Chart, and review the values in the Estimate Results/Detail column.
- Update values in the Work Backlog and Project Attributes tabs as well as the Engagement Scope values in the Reference Sizing Chart.
Note: See how those changes influence the MLP Duration and Hours estimated to complete the first project release and full program.
Confirm your work
For additional information on the Case Type Backlog, see The Case Type Backlog and it place in Pega Express methodology. and Creating a platform Case Type Backlog.
This Challenge is to practice what you learned in the following Module:
Available in the following mission:
Want to help us improve this content?